
Big Data is a collection of knowledge and information that is huge in volume. It is a collection of data in enormous volume yet growing rapidly with time. Big Data is so large and complex that none of the traditional data management tools can efficiently store or process it.
One of the biggest streaming platforms, Netflix also uses big data to complete and process the enormous amounts of information it gathers from its users. According to Sandvine, Netflix accounted for almost 9.39% of downstream internet traffic worldwide in the first half of 2022.
Amazon is another business giant that uses big data for its vast e-commerce operations. They store every single bit of data related to their customer behavior and use this data to analyze purchase patterns and optimize their social media advertising algorithms.
When it comes to characteristics of big data, there are generally 5 V’s that everyone has to take into account.
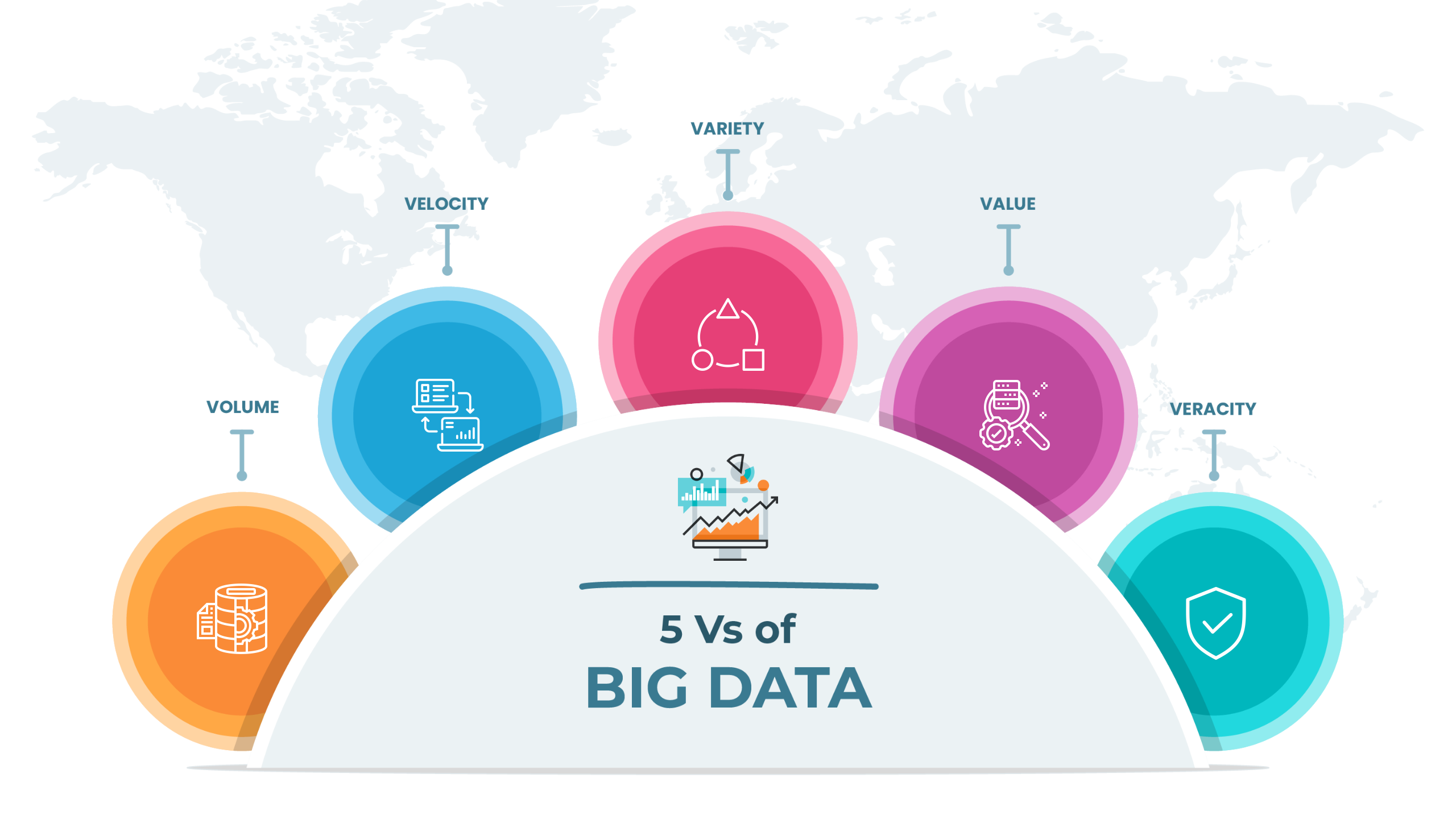
Volume refers to the gigantic amounts of data that a company gathers with its operations. It is the raw data that is yet to be processed to gather intelligent insights. This load of information is collected from different sources like user traffic, IoT devices, social media, videos, financial transactions, and many others.
Velocity refers to the rate at which companies receive, store and manage their data. The velocity of big data directly affects the processing power of the information as only after analysis and processing, the data can meet the demands of users.
Variety alludes to the diversity and degree of different data types, sources, and nature. It includes unstructured data, semi-structured data, and raw/unprocessed data. The data sources might be in the form of photos, videos, text files, PDFs, spreadsheets, and databases.
No matter the velocity or variety of your big data, if the information is unreliable. Value is a critical characteristic that needs to be taken care of to generate an effective and reliable result.
Similar to the Value characteristic, the veracity of big data refers to the trustworthiness of the information. This helps in building a level of confidence in your result. Hence, to generate an effective result, it is vital to sort out the unnecessary information from the necessary one.
Any data which can be stored, accessed, and processed within the sort of fixed format is termed 'structured' data.
Over the decades, computing capabilities have succeeded in developing techniques for working with big data and extracting value from it. However, nowadays, we are experiencing issues when the size of such data grows to a massive extent. Typical sizes are within the craze of multiple zettabytes.
Data with an unknown form or structure is considered unstructured data. In addition to the vast dimensions, unstructured data poses multiple challenges in its processing for deriving value from it.
A typical example of unstructured data may be a heterogeneous data source containing a combination of simple text files, images, videos, etc. Now, organizations have a wealth of knowledge available to them, but unfortunately, they do not have the skills to derive value from it since this data is in its raw or unstructured format.
Semi-structured data can contain both sorts of data. We can see semi-structured data as a structured form, but it's actually not defined with, e.g., a table definition in relational DBMS. An example of semi-structured data may be data represented in an XML file.
Discover the most interesting topic