Stay updated on the newest technologies, recent developments, and latest trends in Analytics and BI

Now you can enjoy the quick and hassle-free configuration of your workspaces with Kockpit’s pre-configured images. Airflow is a virtual machine image (VMI) created for Ubuntu and Red Hat (OS) that allows you to set up your machines within minutes.
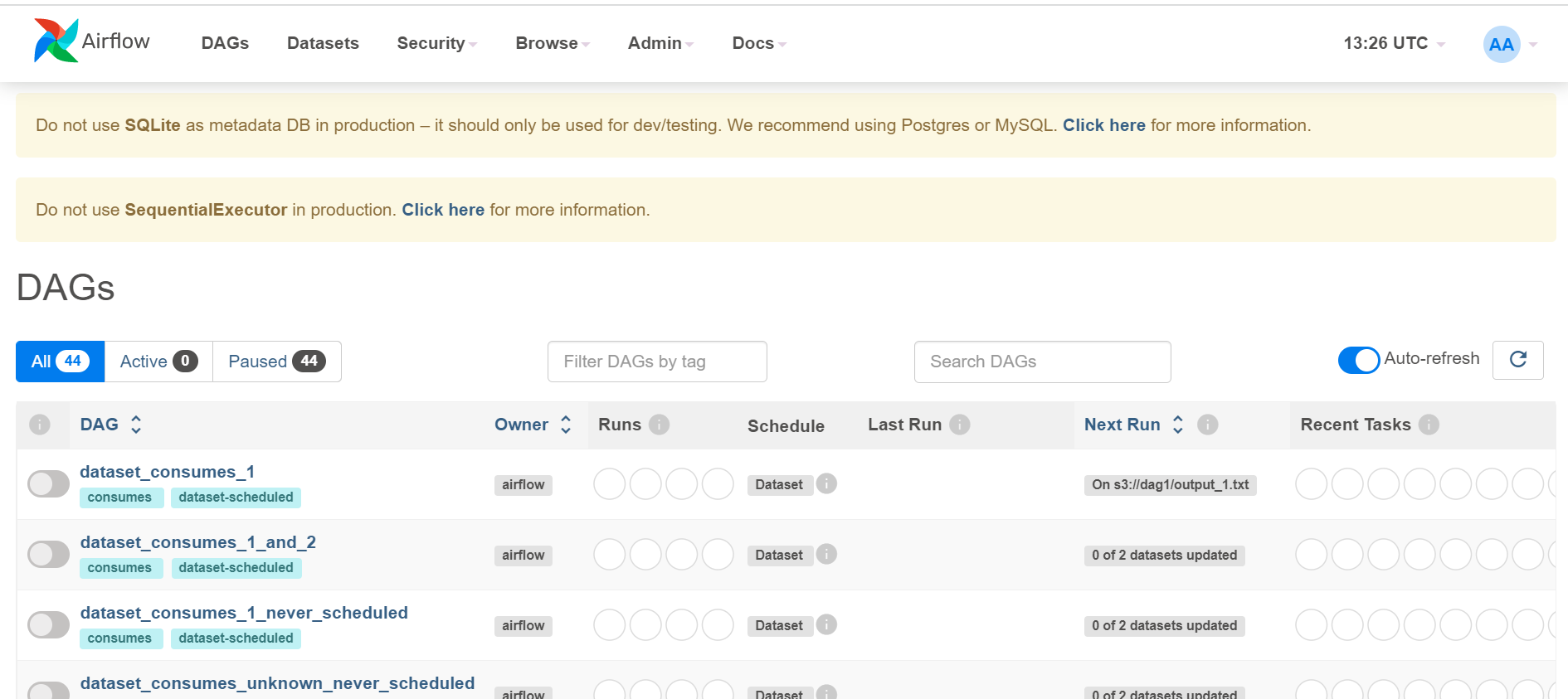
Here, we have packed Airflow in a virtual machine. In this VMI, users need to run “autostart.sh” script inside “/usr/local” directory, and airflow will be up and running, and users can check airflow web UI on their browser.
Airflow is a platform to programmatically author, schedule, and monitor workflows. It has a modular architecture and uses a message queue to orchestrate an arbitrary number of workers. As a result, airflow is ready to scale to infinity.
Airflow pipelines are defined in Python, allowing for dynamic pipeline generation. This allows for writing code that instantiates pipelines dynamically. Easily define your own operators and extend libraries to fit the level of abstraction that suits your environment.
The distribution of Airflow is based on Linux and is provided by Kockpit Analytics Pvt. Ltd. Airflow Image is designed for Production Environments on Azure.
Log in to your Ubuntu VM using SSH.
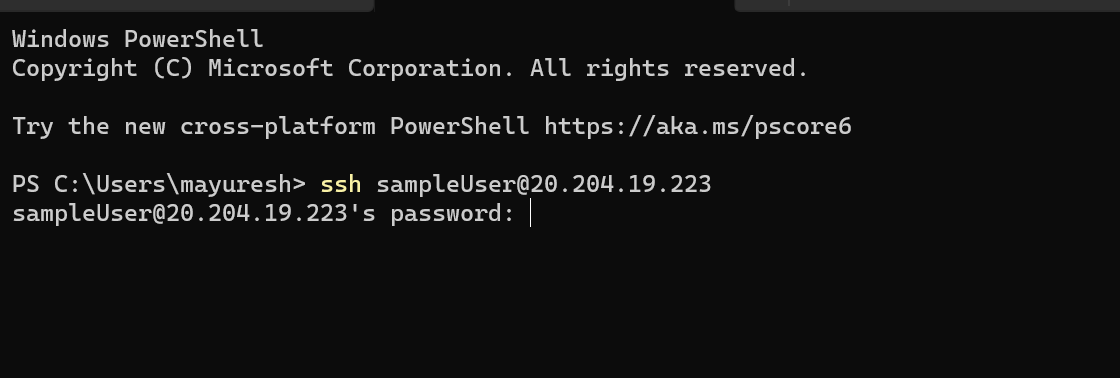
After logging into your VM, type the “cd /usr/local” command to enter the main working directory.
Type the “ls” command to show all the files in the current directory.
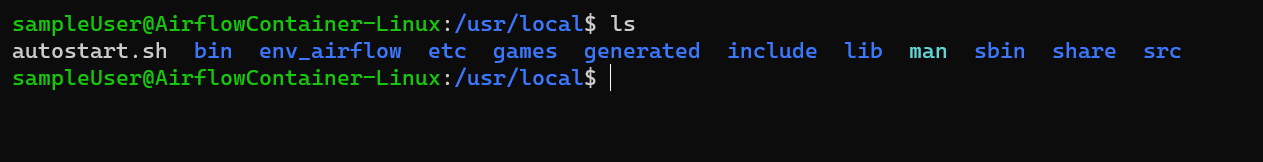
Type “bash autostart.sh,” and you will see airflow running.

Open a web browser on your desktop. Write down your VM’s IP in the address bar followed by “:” and then the port number at which the image is active.
For Example: 20.204.19.121:8181
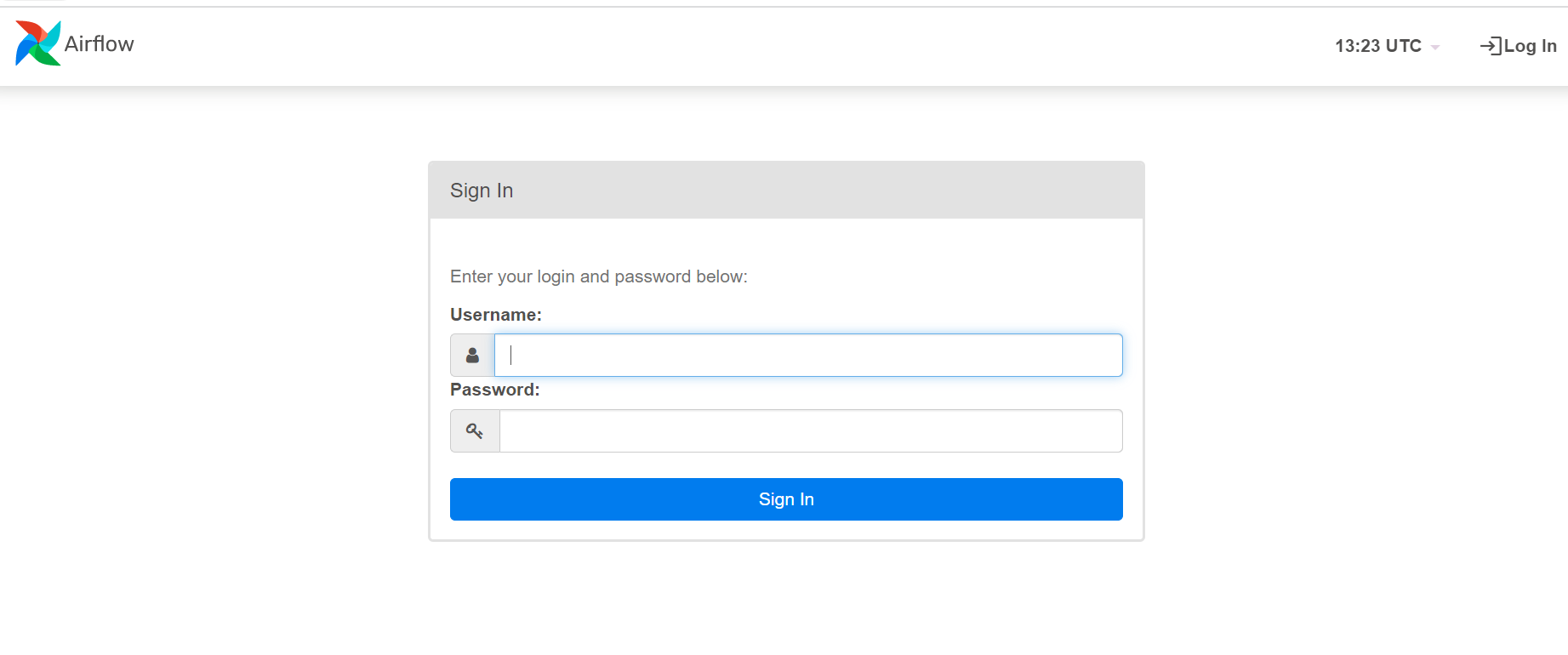
Enter the username and password for the airflow webserver.
The username and password for Airflow are
Username: “admin”
Password: “admin”
After logging in, you can see the Airflow UI. Airflow is started and ready to use.